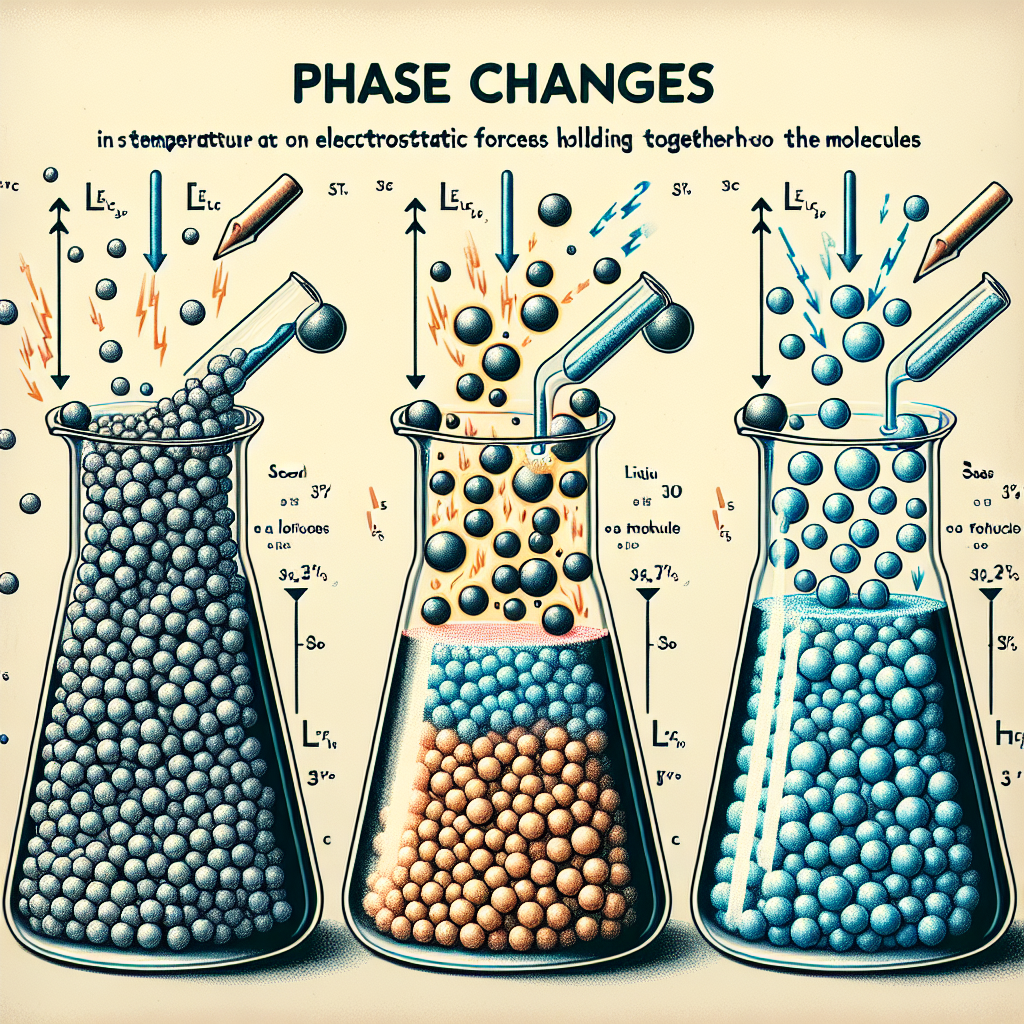
Which statement about the temperatures of phase changes and electrostatic forces holding the molecules is correct?(1 point)
The strength of the forces between molecules in a substance is strongest at higher temperatures
The strength of the forces between molecules in a substance is strongest at higher temperatures
The temperatures at which a substance changes phases is dependent of the size of the molecules in the substance.
The temperatures at which a substance changes phases is dependent of the size of the molecules in the substance.
The temperatures at which a substance changes phases indicate the relative strength of the forces between molecules in the substance.
The temperatures at which a substance changes phases indicate the relative strength of the forces between molecules in the substance.
The strength of the forces between molecules in a substance depends on the number of filled electron shells
Which list shows the phases of matter in order from strongest collective electrostatic forces to weakest collective electrostatic forces?(1 point)
gas, liquid, solid
gas, liquid, solid
gas, solid, liquid
gas, solid, liquid
liquid, solid, gas
liquid, solid, gas
solid, liquid, gas
Which change happens when water boils?(1 point)
The forces between water molecules break, and the bonds between the atoms in water are unchanged.
The forces between water molecules break, and the bonds between the atoms in water are unchanged.
The forces between water molecules become stronger, and the bonds between atoms in the water remain unchanged.
The forces between water molecules become stronger, and the bonds between atoms in the water remain unchanged.
The forces between water molecules are unchanged, and the bonds between the atoms in the water break.
The forces between water molecules are unchanged, and the bonds between the atoms in the water break.
The forces between water molecules and the bonds between the atoms in the water molecules break.
A sample of calcium carbonate is cooled. Which change happens to the molecules of calcium carbonate in the sample?(1 point)
The molecules break apart and then form stronger forces.
The molecules break apart and then form stronger forces.
The forces strengthen, and the molecule structure becomes more rigid.
The forces strengthen, and the molecule structure becomes more rigid.
The molecules vibrate more and weaken the forces.
The molecules vibrate more and weaken the forces.
The forces weaken, and the molecules move around.
The forces weaken, and the molecules move around.
The boiling point of acetone is lower than the boiling point of ethanol. Based on this information, which conclusion can be drawn about the two substances?(1 point)
The intermolecular forces in ethanol are stronger than the intermolecular forces in acetone.
The intermolecular forces in ethanol are stronger than the intermolecular forces in acetone.
The intermolecular forces in acetone are stronger than the intermolecular forces in ethanol.
The intermolecular forces in acetone are stronger than the intermolecular forces in ethanol.
The intramolecular bonds in ethanol are stronger than the intramolecular bonds in acetone.
The intramolecular bonds in ethanol are stronger than the intramolecular bonds in acetone.
The intramolecular bonds in acetone are stronger than the intramolecular bonds in ethanol.
1) The temperatures at which a substance changes phases indicate the relative strength of the forces between molecules in the substance.
2)solid, liquid, gas
3)The forces between water molecules break, and the bonds between the atoms in water are unchanged.
4)The forces strengthen, and the molecule structure becomes more rigid.
5)The intermolecular forces in ethanol are stronger than the intermolecular forces in acetone.
just took it. you're welcome.
Thank You so much.
To anyone else, L is right!
Why did the molecule go to school? Because it wanted to gain some bonds of knowledge!
In response to your first statement, the correct answer is: "The temperatures at which a substance changes phases indicate the relative strength of the forces between molecules in the substance." So, it's like a temperature gauge for molecular strength!
Now, let's tackle the second question. The correct answer for the phases of matter in order from strongest collective electrostatic forces to weakest collective electrostatic forces is: "solid, liquid, gas." So, as the phases change, the electrostatic forces start to loosen up, just like hugging a melting ice cube!
As for what happens when water boils, the correct answer is: "The forces between water molecules break, and the bonds between the atoms in water are unchanged." It's like a molecular dance party where the bonds stay strong, but the forces between the molecules break it down!
Let's move on to the cooling of calcium carbonate. The correct answer is: "The forces weaken, and the molecules move around." It's like a chilly day where the forces become weak, and the molecules start doing a little dance to keep warm!
Finally, when it comes to the boiling points of acetone and ethanol, the correct conclusion is: "The intermolecular forces in ethanol are stronger than the intermolecular forces in acetone." It's like comparing two friends who are competing in a strong handshake contest, and ethanol comes out as the winner!
Hope that brings some laughter and clarity to your questions!
To answer these questions, we need to understand the concepts of phase changes, intermolecular forces, and intramolecular bonds.
1. Which statement about the temperatures of phase changes and electrostatic forces holding the molecules is correct?
The correct statement is: "The temperatures at which a substance changes phases indicate the relative strength of the forces between molecules in the substance."
To understand this, we need to know that phase changes occur when the intermolecular forces between molecules are either overcome or strengthened. When substances change phases, it means that the arrangement of molecules and their interactions change.
The temperature at which a substance changes phases (melting, boiling, or condensing) depends on the strength of the intermolecular forces between molecules. Higher temperatures generally indicate stronger intermolecular forces, and vice versa. So, the statement that the temperatures at which a substance changes phases indicate the relative strength of the forces between molecules in the substance is correct.
2. Which list shows the phases of matter in order from strongest collective electrostatic forces to weakest collective electrostatic forces?
The correct answer is: "solid, liquid, gas"
To determine the order from strongest to weakest collective electrostatic forces, we need to understand that solids have the strongest forces holding their particles together. The molecules in a solid are tightly packed, forming a fixed structure due to strong intermolecular forces. In a liquid, the particles have weaker forces between them, allowing them to move and flow more freely. In a gas, the particles have the weakest intermolecular forces, leading to high mobility and no fixed structure.
So, the correct order is solid (strongest forces) -> liquid (weaker forces) -> gas (weakest forces).
3. Which change happens when water boils?
The correct answer is: "The forces between water molecules break, and the bonds between the atoms in water are unchanged."
When water boils, it transitions from a liquid phase to a gaseous phase. This phase change occurs when the intermolecular forces between water molecules (hydrogen bonding in this case) are overcome by increasing the temperature. As the temperature rises, the forces holding the water molecules together weaken, and eventually, the forces break, allowing the water molecules to escape as water vapor. However, the bonds between the atoms in a water molecule (H2O) remain unchanged. Only intermolecular forces are affected by boiling, not the intramolecular bonds.
4. A sample of calcium carbonate is cooled. Which change happens to the molecules of calcium carbonate in the sample?
The correct answer is: "The forces strengthen, and the molecule structure becomes more rigid."
When a sample of calcium carbonate is cooled, the intermolecular forces between the molecules (ionic bonds in this case) strengthen. Cooling reduces the kinetic energy of the molecules, causing them to slow down and come closer, resulting in stronger intermolecular forces. The crystal structure of calcium carbonate becomes more rigid as the forces holding the molecules together become stronger.
5. The boiling point of acetone is lower than the boiling point of ethanol. Based on this information, which conclusion can be drawn about the two substances?
The correct conclusion is: "The intermolecular forces in ethanol are stronger than the intermolecular forces in acetone."
The boiling point of a substance is directly related to the strength of its intermolecular forces. A higher boiling point indicates stronger intermolecular forces, while a lower boiling point indicates weaker intermolecular forces.
In this case, since acetone has a lower boiling point than ethanol, it means that acetone has weaker intermolecular forces compared to ethanol. Acetone has dipole-dipole forces, while ethanol has stronger hydrogen bonding between its molecules. Hydrogen bonding is a stronger intermolecular force than dipole-dipole forces, which is why ethanol has a higher boiling point compared to acetone.
Therefore, the intermolecular forces in ethanol are stronger than the intermolecular forces in acetone.
A
A
B
A
A
wait is it:
C
D
C
A
B
????